A CT texture-based nomogram for predicting futile reperfusion in patients with intraparenchymal hyperdensity after endovascular thrombectomy for acute anterior circulation large vessel occlusion
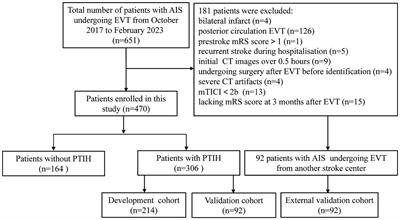
Background: Post-thrombectomy intraparenchymal hyperdensity (PTIH) in patients with acute anterior circulation large vessel occlusion is a common CT sign associated with a higher incidence of futile reperfusion (FR). We aimed to develop a nomogram to predict FR specifically in patients with PTIH. Methods: We retrospectively collected information on patients with acute ischemic stroke who underwent endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) at two stroke centers. A total of 398 patients with PTIH were included to develop and validate the nomogram, including 214 patients in the development cohort, 92 patients in the internal validation cohort and 92 patients in the external validation cohort.
The nomogram was developed according to the independent predictors obtained from multivariate logistic regression analysis, including clinical factors and CT texture features extracted from hyperdense areas on CT images within half an hour after EVT.
The performance of the nomogram was evaluated with integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), category-free net reclassification improvement (NRI), the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC), calibration plots, and decision curve analyses for discrimination, calibration ability, and clinical net benefits, respectively. Results: Our nomogram was constructed based on three clinical factors (age, NIHSS score and ASPECT score) and two CT texture features (entropy and kurtosis), with AUC-ROC of 0.900, 0.897, and 0.870 in the development, internal validation, and external validation cohorts, respectively. NRI and IDI further validated the superior predictive ability of the nomogram compared to the clinical model.
The calibration plot revealed good consistency between the predicted and the actual outcome.
The decision curve indicated good positive net benefit and clinical validity of the nomogram. Conclusion: The nomogram enables clinicians to accurately predict FR specifically in patients with PTIH within half an hour after EVT and helps to formulate more appropriate treatment plans in the early post-EVT period.
Read the full article at the original website
References:
