Animal-derived natural products for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy: current evidence and future perspectives
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has a high morbidity and mortality rate, and the survival rate of HCC patients remains low.
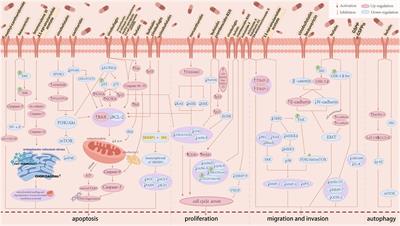
Animal medicines have been used as potential therapeutic tools throughout the long history due to their different structures of biologically active substances with high affinity to the human body. Here, we focus on the effects and the mechanism of action of animal-derived natural products against HCC, which were searched in databases encompassing Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, Science Direct, Springer Link, and EBSCO. A total of 24 natural products from 12 animals were summarized. Our study found that these natural products have potent anti-hepatocellular carcinoma effects.
The mechanism of action involving apoptosis induction, autophagy induction, anti-proliferation, anti-migration, and anti-drug resistance via phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/ protein kinase B (Akt)/ mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), Ras/ extracellular signal regulated kinases (ERK)/ mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), Wnt/β-catenin, and Janus kinase (JAK)/ signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathways. Huachansu injection and sodium cantharidate have been used in clinical applications with good efficacy. we review the potential of animal-derived natural products and their derivatives in the treatment of HCC to date and summarize their application prospect and toxic side effects, hoping to provide a reference for drug development for HCC.
Read the full article at the original website
References:
