Anti-inflammatory and/or immunomodulatory activities of Uncaria tomentosa (cat's claw) extracts: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vivo studies
Background: Uncaria tomentosa (Willd.ex Schult.) DC.(Rubiaceae), is traditionally used by Amazonian indigenous groups to treat inflammatory diseases.
s. To date, there are no systematic reviews and meta-analyses on the use of U. tomentosa for inflammation control in animals supporting the traditional knowledge about this species. To evaluate the effect of U. tomentosa extracts in modulating inflammatory mediators, and to determine which types of inflammatory diseases can be treated by this species. Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies published before July 26th, 2023, identified in PubMed, Embase, and Scopus. Four independent reviewers extracted the data and assessed the risks of bias.
The effects of U. tomentosa on inflammatory diseases and the inflammatory mediators involved were extracted from the studies. Standardized (SMD) mean differences and 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) of the outcomes were estimated.
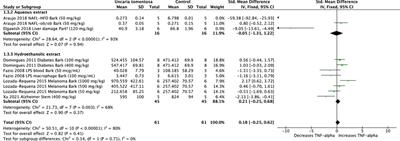
The meta-analyses were conducted using RevMan 5.4 (Cochrane Collaboration). This protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42023450869). Results: Twenty four of 523 studies were included. U. tomentosa extracts decreased the cytokines interleukin (IL)-6 (SMD: –0.72, 95%CI: –1.15, –0.29, p = 0.001), and transcription factor nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) (SMD: –1.19, 95%CI: –1.89, –0.48, p = 0.001). However, the extracts did not significantly alter IL-1 (SMD: –0.16, 95%CI: –0.87, +0.56, p = 0.67), IL-10 (SMD: –0.05, 95%CI: – 0.35, 0.45, p = 0.80) or tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) levels (SMD: 0.18, 95%CI: –0.25, 0.62, p = 0.41). Conclusion: Many extracts of stem bark, roots, and leaves of U. tomentosa, mostly aqueous and hydroethanolic, exhibited anti-inflammatory and/or immunomodulatory activities and low toxicity.
The extracts decreased NF-κB and IL-6.
These findings suggest that this species have potential to treat inflammatory diseases in which these markers are increased, according to the ethnopharmacological use.
These activities are not related to a specific class of compounds. .
Read the full article at the original website
References:
