Early sexual activity lowers the incidence of Intracranial aneurysm: a Mendelian randomization investigation
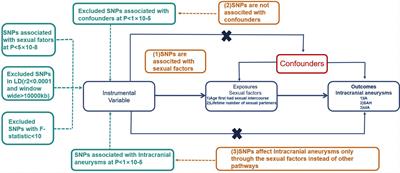
Objective:Investigate the potential correlation between the age of initial sexual contact,the lifetime accumulation of sexual partners,and the occurrence of intracranial aneurysm (IA) employing a two-sample Mendelian randomization approach.Methods:This research aims to elucidate the causal relationship between intracranial aneurysm (IA) and sexual variables. Two distinct sexual variables, specifically the age had first sexual intercourse (n = 406,457) and the lifetime number of sexual partners (n = 378,882), were employed as representative parameters in a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study. Outcome data from 23 cohorts, comprising 5140 cases and 71934 controls, were gathered through genome-wide association studies (GWAS). To bolster analytical rigor, five distinct methodologies were applied, encompassing MR-Egger technique, weighted median, inverse variance weighted, simple modeling, and weighted modeling.Our investigation unveiled a causal relationship between the age first had sexual intercourse and the occurrence of intracranial aneurysm (IA), employing the Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW) approach (Odds Ratio [OR]: 0.609, p-value: 5.684E-04, 95% Confidence Interval [CI]: 0.459 -0.807). This association was notably significant in the context of unruptured intracranial aneurysms (uIA) using the IVW approach (OR: 0.392, p-value: 6.414E-05, 95% CI: 0.248 -0.621).Conversely, our findings did not reveal any discernible link between the lifetime number of sexual partners and the occurrence of IA (IA group:.
Read the full article at the original website
References:
