Self-Perceived Relations Between Artistic Creativity and Mental illness: a Study into Lived Experiences
Aim: To explore the self-perceived relationships between experiences of creativity and mental illness and to understand the meanings behind these relationships.
Background: The idea that mental illness and artistic creativity are somehow related dates back to ancient times.
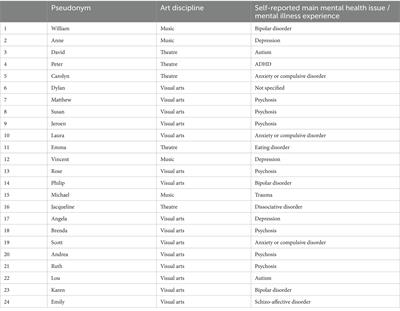
There is some evidence for an actual correlation, but many questions remain unanswered on the nature and direction of the relationship. Qualitative contributions to the debate are scarce, and mainly focus on the potential benefits of participation in the arts for people with mental illness. Design: An explorative, interpretive study. Methods: Twenty-four professional and semi-professional artists with self-reported experience with mental illness, were recruited purposively. Unstructured in-depth interviews were conducted and transcripts were subjected to interpretive analysis, guided by a hermeneutic phenomenological frame. Results: Participants experience a range of interactions between artistic creativity and mental illness. Three constitutive patterns describe what these interactions look like: "flow as a powerful force"; "ambiguous self-manifestation"; and 'narrating experiences of suffering'. Conclusion: The findings show that both the concept of creativity and the concept of mental illness, as well as their interrelationships, are layered and complex phenomena that can take on different meanings in people's lives.
The findings provide starting points for further research that goes beyond the polarized academic debate. Understanding the experiences of artists with mental illness can help shape the role of art in public mental health and mental health care.
Read the full article at the original website
References:
