DTI-ALPS index decreased in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Backgrounds: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has become a significant global public health issue, characterized by a rising prevalence and associated deficits across multiple organ systems.
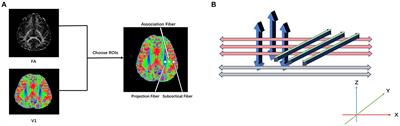
Our study aims to utilize the DTI-ALPS technique to assess the change of ALPS index in T2DM patients, and to explore whether such changes are correlated with cognition level and diffusion parameters. Methods: The study involved 41 patients with T2DM(mean age, 60.49±8.88 years) and 27 healthy controls(mean age, 58.00±7.63 years). All subjects underwent MRI examination, cognitive assessment, and laboratory tests. Tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) was used to evaluate white matter changes. GLM was performed to check the DTI-ALPS index difference between T2DM and HC groups. Spearman correlation analysis and partial correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between the DTI-ALPS index, diffusion properties, cognitive scales. Results: The results show that the ALPS index was lower in T2DM patients. MoCA score was significantly correlated with the ALPS index. Patients with T2DM had a significant increase in both mean diffusivity (MD) and radial diffusivity (RD) and decrease in fractional anisotropy (FA) in these clusters compared to the HC group. Conclusions: The results suggest that the ALPS index is decreased in T2DM patients and associates with cognitive level..
Read the full article at the original website
References:
